GLOBAL FINANCIAL CRISIS - 2008
GLOBAL FINANCIAL CRISIS-2008


The financial crisis of 2008 commenced in the USA but the whole world witnessed the crisis.
COMMENCEMENT - 2001
The commencement of the global financial crisis has its roots connected to 2001 when the Federal bank of USA reduced the interest rate from 6.5% to 2.5% in 2001. This led to a gradual increase in borrowings. The easy availability of credit incentivised people to borrow loans and purchase homes. This led to an increase in home prices.
All this started forming a real estate bubble. Even after witnessing the massive increase in real estate prices and borrowings, the federal bank reduced the interest rate to 1% in 2003.
THE FINAL CALL
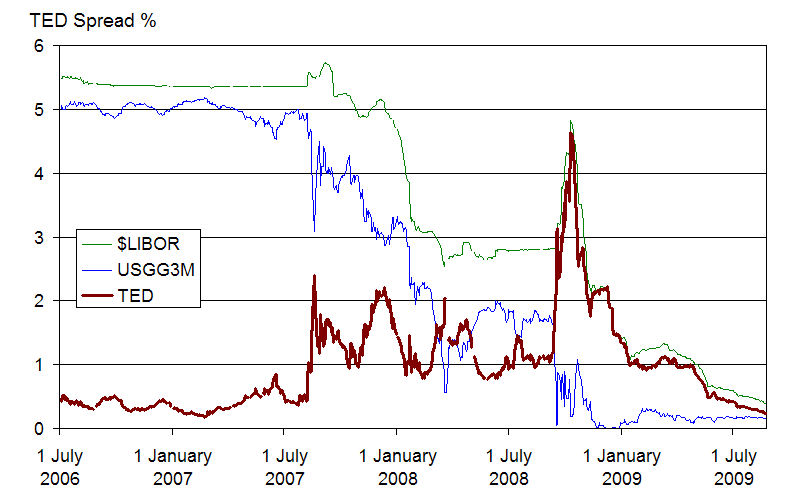
From 2004, there was a sharp increase in interest rates in the USA. From 2004 fed rates had reached 5.25%which continued till 2007, following this the home prices started declining. Borrowers were not able to pay the interest, and many sub prime lenders had to file for bankruptcy.
The biggest shock was when “Lehman Brothers”, one of the biggest global banks filed for bankruptcy. The banks ran out of their reserves. Even though the central banks were providing liquidity support, many lenders filed for bankruptcy.
There was a massive decrease in employment rate all over the world. Over 2.6 million employees lost their jobs in 2008. Around 500000 employees lost their job in India due to recession.

ECONOMIC MEASURES TO DEAL WITH CRISIS
In September 2008 American government and federal reserve made a plan to handle the crisis. They decided to buy the troubled assets. This plan was named as a “ troubled asset relief program”, it was signed into law in October 2008.
Most of the firms which got money via TARP have paid it back and until summer 2011 the financial markets stabilized and grew. Also there was reduction in interest rate by fed from 5% to 0%. Interest rate in Japan was even less than 0%.
The reserve bank of India also decreased the interest rate from 7% to 3.25%. The Indian government increased the fiscal deficit from 2.5% of GDP to 6% of GDP in 2009.
It took almost 3-5 years to stabilize the global economy.
Shaurya Gupta
Bcom(hons), Delhi University
Financial Markets(hons), Yale University.



Very informative. Good job .
ReplyDeleteThanks alot
Delete